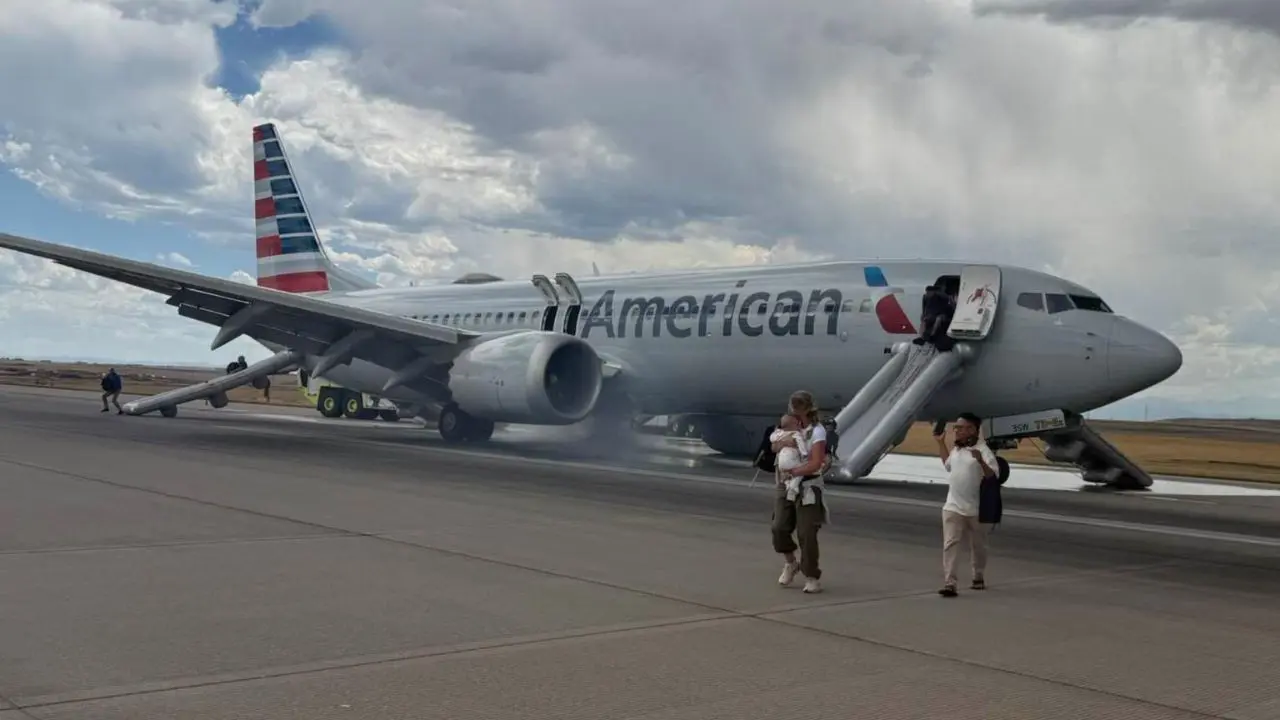
What Happened?
On Saturday, July 26, 2025, around 2:45 p.m. MDT, American Airlines Flight 3023, a Boeing 737 MAX 8 scheduled from Denver International Airport (DEN) to Miami, experienced a critical mechanical issue during takeoff. A blown tire and overheated brake near its rear landing gear triggered smoke and visible flames, prompting the pilots to abort the takeoff immediately.
Emergency slides were deployed, and all 173 passengers and 6 crew members evacuated safely. One passenger was taken to a hospital with minor injuries; five others were treated on-site for smoke inhalation or stress. The Denver Fire Department extinguished the fire within minutes, and the aircraft was removed from service pending inspection.
Incident Data Snapshot
| Detail | Info |
|---|---|
| Flight Number | American Airlines Flight 3023 |
| Aircraft | Boeing 737 MAX 8 |
| Date & Time | July 26, 2025, ~2:45 p.m. MDT |
| Route | Denver (DEN) → Miami (MIA) |
| Onboard | 173 passengers, 6 crew |
| Incident Cause | Tire failure / brake fire |
| Injuries | 1 minor hospitalized, 5 treated onsite |
| Response | Fire extinguished; evacuation via slide |
| FAA / NTSB | Investigation underway |
Why It Happened
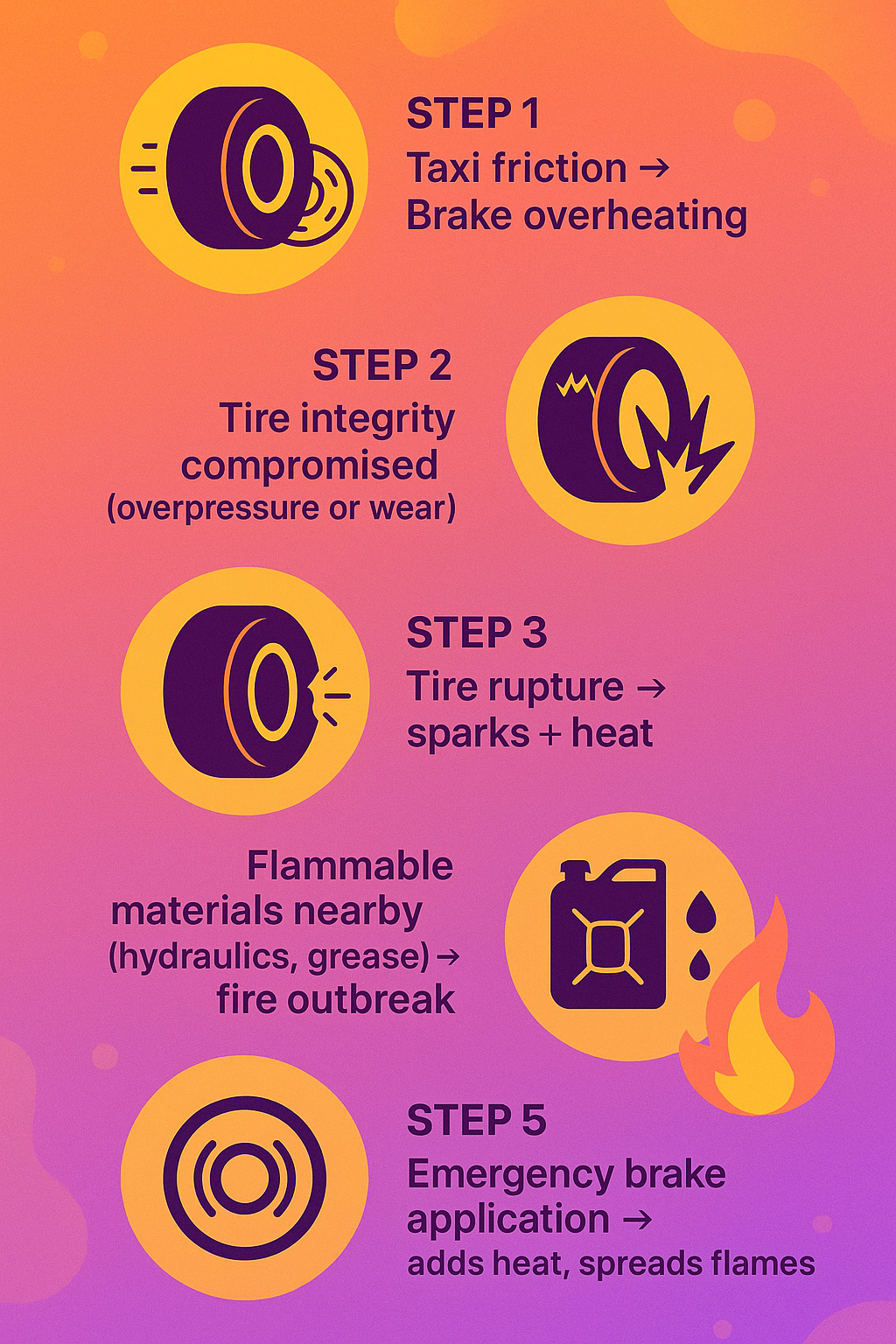
Chain Reaction: Tire Blowout → Brake Fire
Passenger accounts describe a loud boom followed by violent shaking and a sudden leftward veering during the takeoff roll. A landing gear tire apparently exploded, collapsing onto its suspension and triggering intense braking and localized fire near the rear gear.
A Reddit eyewitness wrote:
"Takeoff Aborted: The flight was initially cleared … we heard a loud ‘pop’ … Tire Blowout … pilot immediately began braking."
This cascade of mechanical stress points to two primary failure nodes:
- Overheated brakes, possibly due to prolonged taxiing in hot weather
- Tire overpressure or fatigue, leading to blowout and ignition
The design of modern aircraft allows for fire-resistant materials and heat shields, but in this case, proximity to hydraulic fluid lines may have worsened the fire risk.
Aviation Engineering Context
Boeing 737 MAX 8 landing gear uses carbon brakes that can reach over 1,000°F during intense braking. While safe under normal conditions, extreme heat combined with:
- Delays on taxiways
- Repeated braking
- Improper tire pressure checks
...can create ideal conditions for rupture or spontaneous ignition.
Diagram: How Tire Failures Trigger Fires
Compared: Previous Incidents
- American Airlines Flight 383 (2016): Engine fire on takeoff in Chicago. Resulted in 21 injuries and aircraft write-off.
- British Airtours Flight 28M (1985): Uncontained engine failure and fire during takeoff. Poor evacuation led to 55 deaths.
What’s different in Flight 3023:
- No engine failure
- Fire isolated to gear assembly
- Faster crew response
Global Lessons
- Qatar Airways (2022): Uses real-time tire pressure and brake temp sensors.
- ANA Japan: Requires mandatory cooling periods on overheated brakes before clearance.
Now What?
For Airlines & Maintenance Crews
Install Real-Time Heat and Tire Sensors
FAA should mandate retrofit kits that monitor pressure and brake temperature live.Revise Taxi Brake Protocols
Ground control should stagger clearance for prolonged taxiing flights or impose brake cooldown zones.Audit Pre-Flight Tire Checks
Make tire condition monitoring as rigorous as fuel checks, especially in MAX series aircraft.
For Regulators (FAA/NTSB)
Publish Heat Risk Zones for Airports
Denver, Phoenix, and similar hot-airport hubs need special heat management protocols.Enforce Slide Deployment Training
Refresher simulations every 6 months for all crew on slide evacuation procedures.Mandate Incident Transparency Timelines
Require airlines to publish technical findings within 30 days of fire-related ground events.
For Passengers
Never Grab Luggage During Evacuation
In Flight 3023, some passengers delayed escape by retrieving bags — this can kill.Memorize Nearest Exit & Count Rows
In smoky conditions, visual cues fail. Row-counting gives a survival edge.Demand Safety Demonstrations
If a crew skips the demo, ask. Familiarity with slide use and brace positions saves lives.
Final Thoughts
The Flight 3023 scare is a powerful reminder that even well-maintained aircraft can encounter cascading failures from routine operations. When these events occur, only three things matter: trained crew, decisive action, and informed passengers.
The real heroes are not just the fire department or the pilots — but also the passengers who listened, stayed calm, and didn’t turn a fire into a stampede. The future of air safety lies not just in tech upgrades but in human readiness.
Source : AP News


